Diets like the Keto, Paleo and Atkins focus on high-fat, high-protein meals that are often low in carbohydrates. This mix may appeal to Clostridioides difficile bacteria, too.
In a new study published this in mSystems, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, researchers report that mice fed a high-protein, high-fat diet were more likely to acquire a deadly C. difficile infection than mice eating a standard diet. Their findings also suggest that a diet high in carbohydrates protects against infection.
Every year in the United States, hundreds of thousands of people are diagnosed with C. difficile infections and more than 10,000 die, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Taking antibiotics increases a person’s risk of infection.
The researchers behind the new work caution that their study was done on mice and additional research is needed to establish a connection between these diets and infections in people. At the same time, they argue, it’s an avenue of research that’s important to explore. And, even the researchers said they would probably change their diet while on antibiotics.
Western diets would seem to favor CDI since they are enriched in both proteins and simple sugars and yet are deficient in microbiota-accessible carbohydrates (MACs) and other fiber sources, and rates of CDIs are indeed highest in developed countries. A separate study found that mixtures of MACs, or, specifically, inulin, decreased C. difficile burdens in humanized mice, while stimulating growth of carbohydrate-utilizing microbes and SCFA production
“We have to look at humans to see if it correlates,” said chemist Ernesto Abel-Santos, Ph.D., at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV). “We know that people have been following these different extreme diets and we really don’t have a good handle on what these changes are doing to our systems.”
“We know very well that diet affects the gut microbiome,” added microbiologist Brian Hedlund, Ph.D., also at UNLV. Hedlund and Abel-Santos co-led the new study.
The group studied 4 groups of mice with 5 animals each. Each group received antibiotics and was fed a different diet: one was high-fat, high-protein; another was high-fat, low-protein; a third was high-carbohydrate; and the fourth was a standard laboratory diet for experimental mice.
The results were startling:
- In the high-protein, high-fat group, all the animals developed severe infections and died within 4 days.
- In the high-fat, low-protein group, only 2 animals died.
- In the high-carbohydrate group, 2 mice showed mild symptoms and recovered and in the standard diet group, all of the animals showed signs of infection but also recovered.
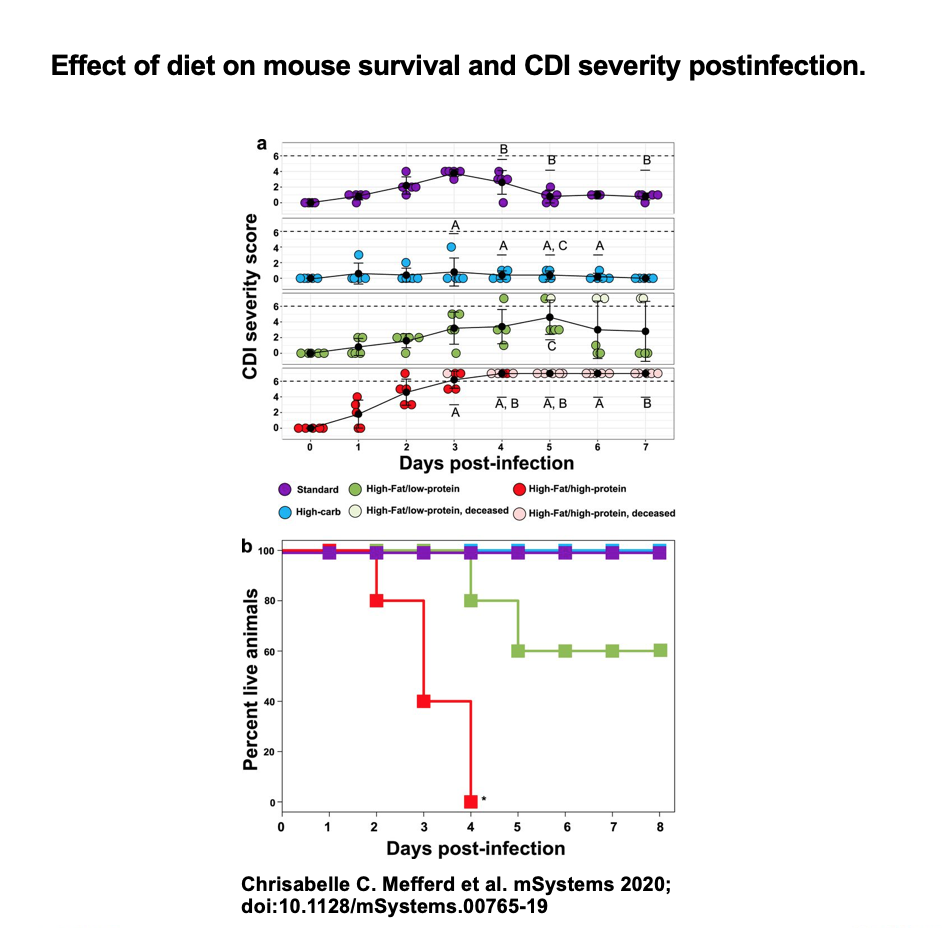
Recent studies suggest that because antibiotics kill bacteria species indiscriminately, the medications decimate populations of organisms that compete for amino acids, leaving C. difficile free to propagate. But Hedlund said the story is even more complex. “It’s clear that it’s not just a numbers game,” he said. The new work suggests that diet may promote microbial groups that can be protective, even after antibiotics. For an infection to flourish, he said, “you might need this combination of wiping out C. difficile competitors with antibiotics and then a diet that promotes overgrowth and disease.”
The new study raised questions that the researchers will pursue in future studies. For example: The high-carb diet, which seemed protective against C. difficile infection, gave rise to the least diverse community of microbes. “Lots of papers say that a lower microbial diversity is always a bad thing, but in this case, it had the best disease outcome,” said Abel-Santos. However, he cautions that a high-carb diet could lead to animals becoming asymptomatic carriers that can disseminate the infection to susceptible subjects.
The group will also begin looking at ways to understand the connection between diet and C. difficile infection in people. “Whether this will translate to humans or not, I’m not totally sure,” said Abel-Santos. “But the next time I take antibiotics, I’m not going to be eating a high-protein or Atkins diet.”
Conclusion/ The role of Western and weight-loss diets with extreme macronutrient composition in the risk and progression of CDI is poorly understood. In a longitudinal study, we showed that a high-fat/high-protein, Atkins-type diet greatly exacerbated antibiotic-induced CDI, whereas a high-carbohydrate diet protected, despite the high monosaccharide and starch content. Our study results, therefore, suggest that popular high-fat/high-protein weight-loss diets may enhance CDI risk during antibiotic treatment, possibly due to the synergistic effects of a loss of the microorganisms that normally inhibit C. difficile overgrowth and an abundance of amino acids that promote C. difficile overgrowth. In contrast, a high-carbohydrate diet might be protective, despite reports on the recent evolution of enhanced carbohydrate metabolism in C. difficile.
Click Here for Full Text Study