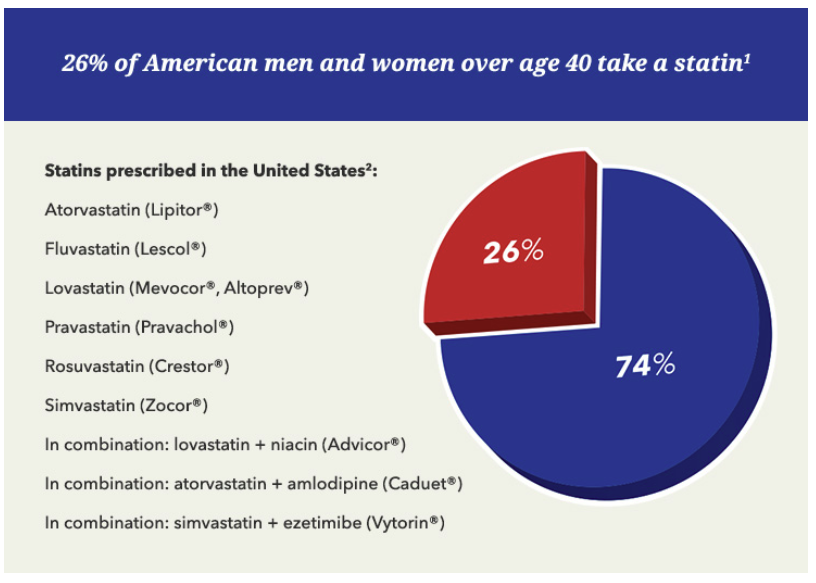
- Use of certain cholesterol-lowering medication is increasing over time1
- Nine out of 10 adults using a cholesterol-lowering medication take a statin1
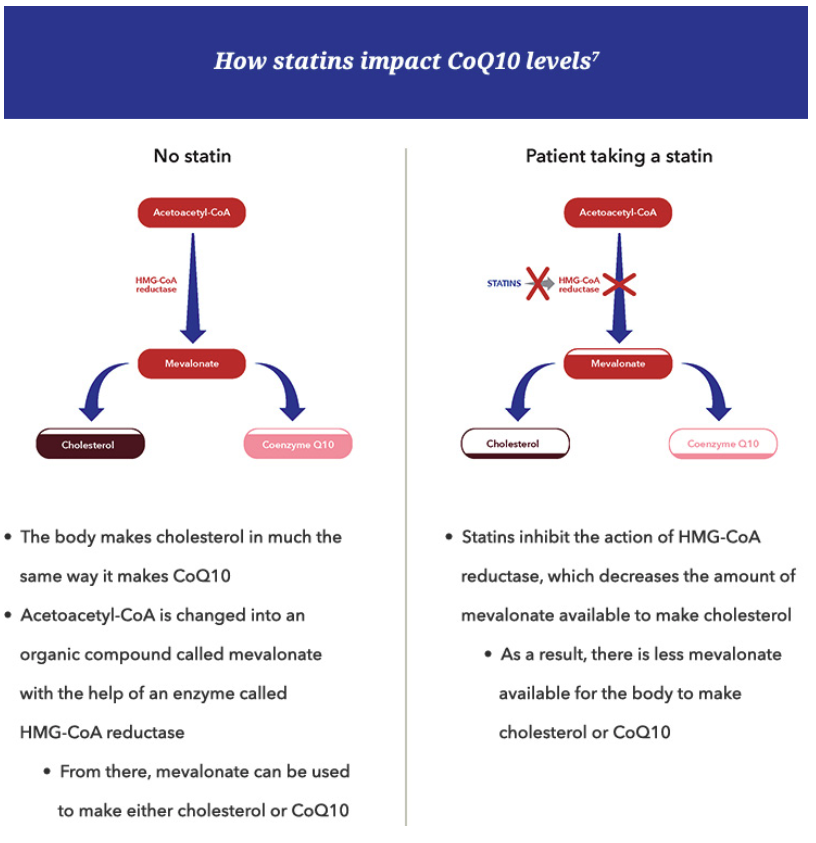
Cholesterol-lowering statins can significantly lower the amount of CoQ10 (ubiquinone) in the blood3-6
- Statins can lower the amount of CoQ10 in the body, even when a patient has taken a standard dose for as few as 3 months3
A side effect of statin administration is depletion of CoQ10, which can lead to muscle-related adverse reactions7
- Daily Ubiquinol supplementation effectively restores CoQ10 levels which can help support muscle health during statin use.7,8
In patients with chronic heart failure, adding Ubiquinol to statin therapy can elevate reduced CoQ10 levels, which can support skeletal and cardiac muscle health9“
…there is a strong case for considering co-administration of ubiquinol with statin therapy in patients with depressed or borderline myocardial function.”
“…we believe that the co-administration of 300 mg ubiquinol with the combination ezetimibe/statin should be the preferred initial therapeutic option for LDL-lowering in patients with heart failure and hypercholesterolaemia, especially in those with high oxidative stress and coronary artery disease.”
—Kloer H-U, Belardinelli R, Ou R, Rosenfeldt F. Combining ubiquinol with a statin may benefit hypercholesterolaemic patients with chronic heart failure. Heart Lung Circ. 2020;29(2):188-195.
Replenish the CoQ10 levels depleted by statins with Ubiquinol
- Ubiquinol can replenish CoQ10 in patients taking statins7,8
- Ubiquinol is more readily absorbed in the body and is more bioavailable than conventional CoQ1010
- Read more about the absorption and bioavailability of Ubiquinol
- Ubiquinol is the only form of CoQ10 that functions as an antioxidant11
- Read more about how Ubiquinol supports optimal heart health
References
- Gu Q, Paulose-Ram R, Burt VL, Kit BK. Prescription cholesterol-lowering medication use in adults aged 40 and over: United States, 2003-2012. NCHS Data Brief, No 177. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2014.
- American Heart Association. Cholesterol medications. Available at: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/cholesterol/prevention-and-treatment-of-high-cholesterol-hyperlipidemia/cholesterol-medications. Last reviewed November 10, 2018. Accessed December 12, 2018.
- Passi S, Stancato A, Aleo E, et al. Statins lower plasma and lymphocyte ubiquinol/ubiquinone without affecting other antioxidants and PUFA. BioFactors. 2003;18(1-4):113-124.
- De Pinieux G, Chariot P, Ammi-Saïd M, et al. Lipid-lowering drugs and mitochondrial function: effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on serum ubiquinone and blood lactate/pyruvate ratio. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1996;42(3):333-337.
- Mortensen SA, Leth A, Agner E, Rohde M. Dose-related decrease of serum coenzyme Q10 during treatment with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Mol Aspects Med Suppl. 1997;18:S137-S144.
- Watts GF, Castelluccio C, Rice-Evans C, et al. Plasma coenzyme Q (ubiquinone) concentrations in patients treated with simvastatin. J Clin Pathol. 1993;46:1055-1057.
- Zlatohlavek L, Vrablik M, Grauova B, et al. The effect of coenzyme Q10 in statin myopathy. Neuroendocrinol Lett. 2012;33(suppl 2):98-101.
- Fedacko J, Pella D, Fedackova P, et al. Coenzyme Q10 and selenium in statin-associated myopathy treatment. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;91(2):165-170.
- Kloer H-U, Belardinelli R, Ou R, Rosenfeldt F. Combining ubiquinol with a statin may benefit hypercholesterolaemic patients with chronic heart failure. Heart Lung Circ. 2020;29(2):188-195.
- Langsjoen PH, Langsjoen AM. Comparison study of plasma coenzyme Q10 levels in healthy subjects supplemented with ubiquinol versus ubiquinone. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2013;3(1):13-17.
- Forsmark-Andrée P, Ernster L. Evidence for a protective effect of endogenous ubiquinol against oxidative damage to mitochondrial protein and DNA during lipid peroxidation. Mol Aspects Med. 1994;15(suppl 1):S73-S81.