This articles provides two studies that support the use of botanicals for liver health.

Liver disease has been declared a global health issue affecting about 25%. Health issues related to NAFLD alone are projected to cost Americans more than $1 trillion dollars over the next 10 years and result in rising cases of advanced cardiovascular disease and liver failure. In this posting, we offer two studies showing the beneficial use of botanicals, such as bergamot, garlic, ginger and artichoke to address liver health.
Bergacyn may support liver health
Results of a new clinical study show that a bergamot extract bergamot and a high-sesquiterpene extract of artichoke leaf (patented brand Bergacyn®) for digestive and metabolic support, has beneficial effects in reducing the effects of excessive fat in the liver, inflammation, and oxidative stress. The nutraceutical contains a 17% flavonone polyphenol and 5% cynaropicrin content when blended in process with micronized bergamot pulp fibers.
Results of the 16 week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, conducted by Musolino, Gliozzi, Bombardelli, et alia, were published in February in The Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine. For the study, 80 subjects were divided into four treatment subgroups: placebo; 600mg Bergacyn, 600 mg of a stand-alone bergamot extract blend, and an equivalently dosed cynara extract blend. The trial resulted in statistically significant changes of all tested non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)-related parameters for the Bergacyn group, as compared to placebo (p<0.05).
Using the objective biopsy-correlated hepatorenal index (HRI) parameter, liver fat accumulation regressed two levels – from severe to mild – in the Bergacyn group as compared to placebo (p<0.05):
- The patented form of bergamot/artichoke extract differentiated itself from the other interventions by more substantially reducing both AST (aspartate aminotransferase) and ALT (alanine aminotransferase), liver damage enzymes that define the more destructives stages of NAFLD.
- ALT and AST levels were reduced by approximately 15 and 18 points, respectively, (p<0.05) in the Bergacyn group, versus a 10-point average reduction in the stand alone groups (with no changes in the placebo group).
- The bergamot/artichoke extract group also recorded the greatest quantitative increase in antioxidation and fibrosis intervention (via reduced scar tissue mediators) and anti-inflammatory action.
The significantly improved biomarkers were the suggested mechanism in additionally improving endothelial function, particularly for participants with type-2 diabetes.
“Bergacyn’s unique blending of a high-polyphenol extract of bergamot and a high-sesquiterpene extract of artichoke leaf showed a novel synergistic benefit that was more than additive, when compared to stand-alone, single doses of bergamot or cynara extract,” explains Dr. Shavon Jackson-Michel, director of medical and scientific affairs for DolCas. “The potentizing action as a function of the patented process used enhances Bergacyn’s bioactivity.”
Beneficial effects of Chinese herbs for liver health
Abstract/ Chinese herbs and their extracts have been identified as a novel source of potential therapeutic agents in the prevention and treatment of fatty liver disease. Beneficial effects of these herbal medicines mean that they can be classified as novel candidates for the treatment and prevention of both alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), in place of conventional allopathic treatments. In this review, researchers explore the current literature related to herbal medicines used for the treatment of or protection against fatty liver diseases and describe their mechanisms of action.
Numerous Chinese herbs have been shown to exert a medicinal effect on fatty liver disease as well as preventing the accumulation of fat in the liver in the first place. As in all conditions prevention is better than cure, which means that if fatty liver disease can be prevented by the use of hepatoprotective herbs or diet it may help to reduce the burden of this chronic disease on the global health care system. In this review, we explore the current literature pertaining to the prevalence of fatty liver disease, the effect of diet on its development and its risk factors and pathogenesis, as well as reviewing the Chinese herbs that exhibit hepatoprotective effects against fatty liver diseases AFLD and NAFLD.
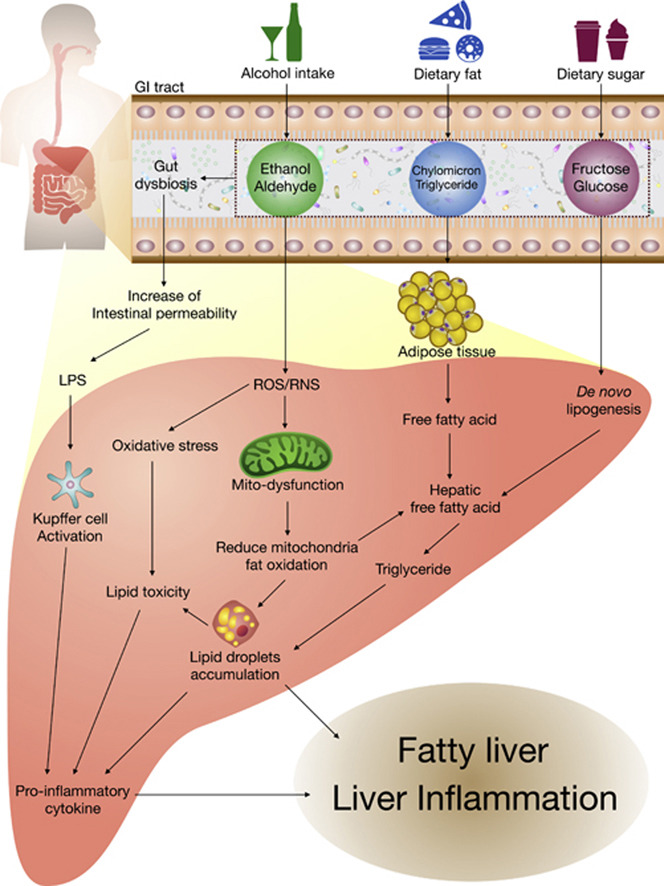
In this study you will learn about the following:
- Effect of diet and other risk factors in the development of fatty liver disease
- Fatty-liver disease pathogenesis
- Mechanism of alcoholic fatty-liver disease
- Mechanism of non-alcoholic fatty-liver disease
- Chinese herbs that exhibit a hepatoprotective effect against AFLD, including garlic, ginger, bitter gourd, lychee, ginseng, Korean pine, and Turuarame extracts.
- Botanicals for NAFLD, such as garlic essential oil, diallyl disulfide, ginger, citral, Damask rose flowers ethanol extract, green tea polyphenols, and ginkgolide A to reduce the concentration of triglycerides, cholesterol, AST and ALT in the blood stream.
Click Here to Download the Full Text Study and a List of Botanicals for Fatty Liver Disease