Ubiquinol significantly improves endothelial function1
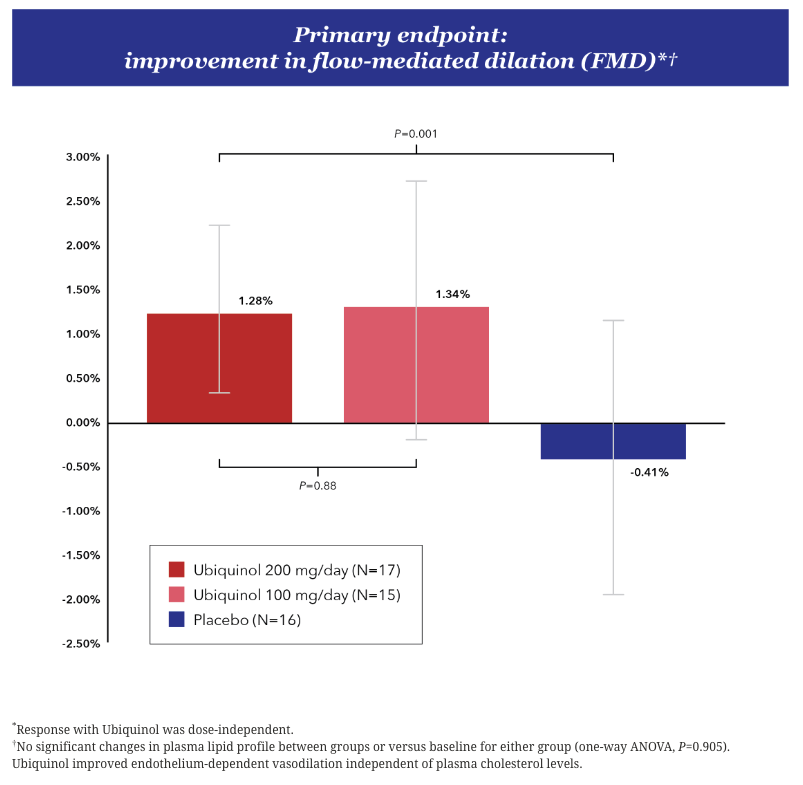
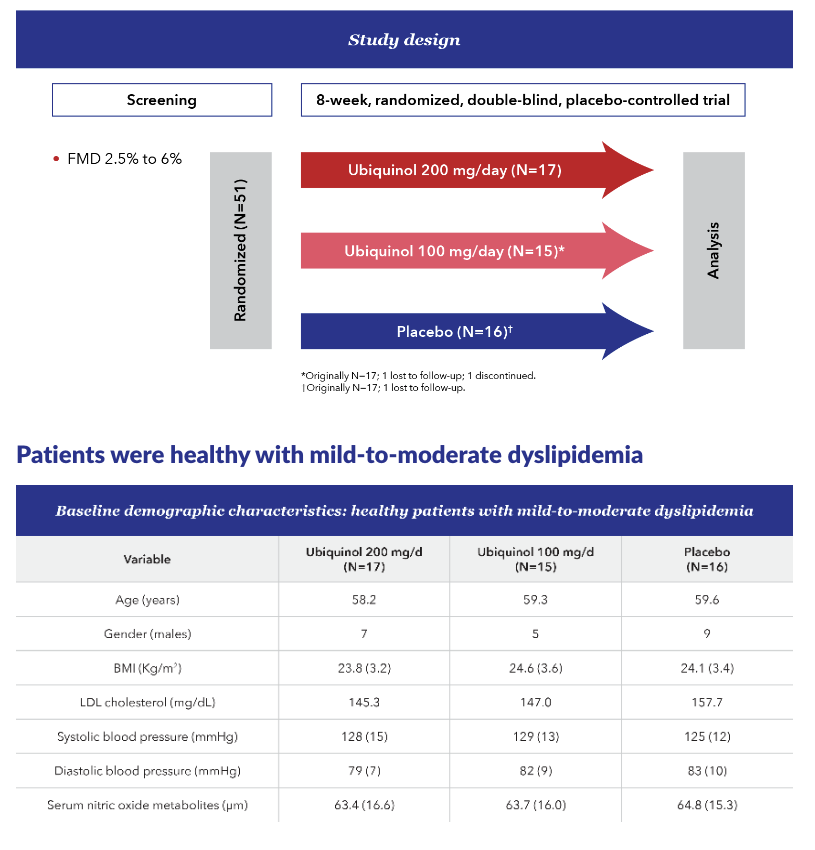
In an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-center trial, with the primary outcome of change in flow-mediated dilation (FMD) in healthy patients with mild-to-moderate dyslipidemia, Ubiquinol significantly improved dyslipidemia-related endothelial dysfunction (P=0.001).
Flow-mediated dilation refers to a measurement of change (widening) of brachial artery diameter following an induced increase in blood flow. FMD reflects nitric oxide-mediated arterial function, and is a measure of blood vessel health.
Cardiovascular health is associated with many factors, including diet, lifestyle and genetics. According to a 2019 expert consensus report, each 1% increase in FMD involves a significant 8% to 13% reduction in the risk of cardiovascular events.2
Significant improvements on 3 secondary endpoints
- Ubiquinol increased plasma CoQ10 levels versus placebo (P<0.001), and reduced the percentage of oxidized CoQ10 (P<0.001)
- Serum NOx increased significantly in all subjects receiving Ubiquinol (P=0.016) versus placebo
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation lag time improved significantly in those receiving 200 mg/day Ubiquinol (P=0.017) versus placebo
The improvement in endothelial function with Ubiquinol was positively correlated with increased NOx concentration (P=0.012) and increased LDL lag time over the course of the study (P=0.031).
Safety profile
No adverse events were reported.
An 8-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Ubiquinol significantly improved endothelial function in cardiac patients with reduced ejection fraction3
In a separate small, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study of 14 patients with HFrEF (heart failure with reduced ejection fraction), Ubiquinol 400 mg/day for 3 months provided significant improvement in peripheral endothelial function.
- Peripheral endothelial function was assessed using the reactive hyperemia index (RHI)
- RHI significantly improved with Ubiquinol (P=0.026) but not with placebo (P=0.198)
References
- Sabbatinelli J, Orlando P, Galeazzi R, et al. Ubiquinol ameliorates endothelial dysfunction in subjects with mild-to-moderate dyslipidemia: a randomized clinical trial. Nutrients. 2020;12(4):1098. doi:10.3390/nu12041098.
- Thijssen DHJ, Bruno RM, van Mil A, et al. Expert consensus and evidence-based recommendations for the assessment of flow-mediated dilation in humans. Eur Heart J. 2019;40:2534-2547. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehz350.
- Kawashima C, Matsuzawa Y, Konishi M, et al. Ubiquinol improves endothelial function in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a single-center, randomized double-blind placebo-controlled crossover pilot study. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2020;20:363-371. doi:10.1007/s40256-019-00384-y.