There is a growing body of evidence to suggest that cannabinoids are beneficial for a range of clinical conditions, including pain, inflammation, epilepsy, sleep disorders, the symptoms of multiple sclerosis, anorexia, schizophrenia and other conditions.
The transformation of cannabinoids from herbal preparations into highly regulated prescription drugs is therefore progressing rapidly. The development of such drugs requires well-controlled clinical trials to be carried out in order to objectively establish therapeutic efficacy, dose ranges and safety.
The low oral bioavailability of cannabinoids has led to feasible methods of administration, such as the transdermal route, intranasal administration and transmucosal adsorption, being proposed. The highly lipophilic nature of cannabinoids means that they are seen as suitable candidates for advanced nanosized drug delivery systems, which can be applied via a range of routes.
Nanotechnology-based drug delivery strategies have flourished in several therapeutic fields in recent years and numerous drugs have reached the market. This review, from the journal Molecules, explores the most recent developments, from preclinical to advanced clinical trials, in the cannabinoid delivery field, and focuses particularly on pain and inflammation treatment (see image below). Likely future directions are also considered and reported.
IMAGE 1
When you download this study, you will learn:
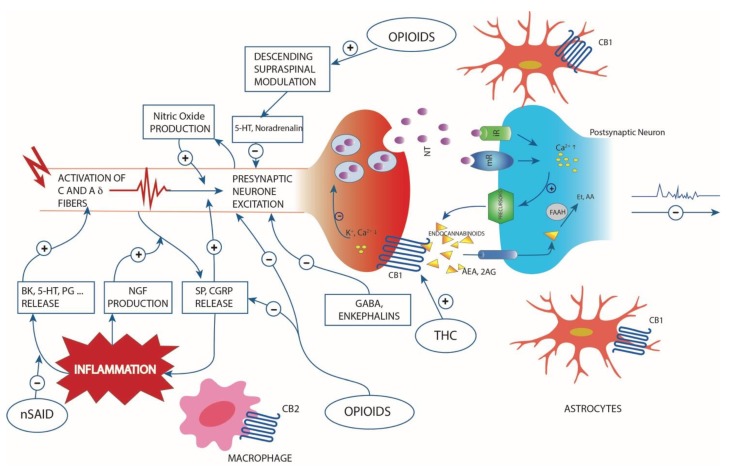
1. Role of Cannabinoids in Inflammation and Pain
2. Current Drug Dosage Forms and Novel Delivery Systems
3. Oral Delivery Systems
4. Mucosa Administration
5. Pulmonary Delivery
6. Topical and Transdermal
7. Lipid Carriers
8. Nanotechnology and Future Developments
To gain access to this article and the rest of our extensive database of full-text articles, please register below or log in here.