Is one’s microbiome composition a question of nature vs nurture? Some microbiome researchers 
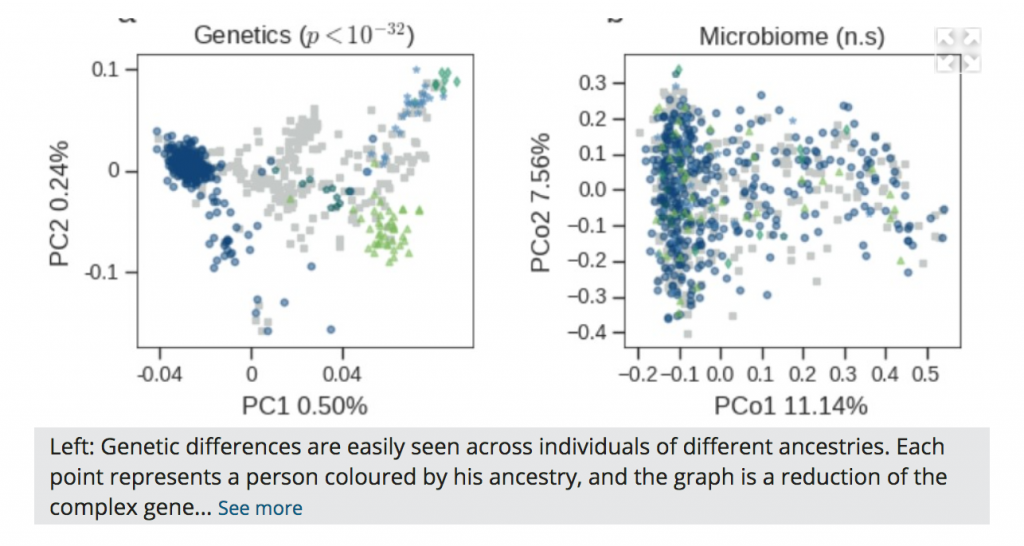
Indeed, the working hypothesis has been that genetics plays a major role in determining microbiome variation among people. According to this view, our genes determine the environment our microbiome occupies, and each particular environment allows certain bacterial strains to thrive. However, the Weizmann researchers were surprised to discover that the host’s genetics play a very minor role in determining microbiome composition – only accounting for about 2% of the variation between populations.
Host genetics has only a minor influence on microbiome variability, which is more strongly associated with environmental factors such as diet. The authors propose a ‘microbiome-association index’ that describes the association of the microbiome with host phenotype. Combining this measurement with host genetic and environmental data improves the accuracy of predictions about several human metabolic traits, such as glucose and obesity traits.
The research was led by research students Daphna Rothschild, Dr. Omer Weissbrod and Dr. Elad Barkan from the lab of Prof. Eran Segal of the Computer Science and Applied Mathematics Department, together with members of Prof. Eran Elinav’s group of the Immunology Department, all at the Weizmann Institute of Science. Their findings were based on a unique database of around 1,000 Israelis who had participated in a longitudinal study of personalized nutrition.
Israel has a highly diverse population, which presents an ideal experimental setting for investigating the effects of genetic differences. In addition to genetic data and microbiome composition, the information collected for each study participant included dietary habits, lifestyle, medications and additional measurements.
Microbiome Composition Study Results
The scientists analyzing this data concluded that diet and lifestyle are by far the most dominant factors shaping our microbiome composition.
If microbiome populations are not shaped by our genetics, how do they nonetheless interact with our genes to modify our health? The scientists investigated the connections between microbiome and the measurements in the database of cholesterol, weight, blood glucose levels, and other clinical parameters. The study results were very surprising: For most of these clinical measures, the association with bacterial genomes was at least as strong, and in some cases stronger, than the association with the host’s human genome.
According to the scientists, these findings provide solid evidence that understanding the factors that shape our microbiome may be key to understanding and treating many common health problems.
We cannot change our genes, but we now know that we can affect – and even reshape — the composition of the different kinds of bacteria we host in our bodies. So the findings of our research are quite hopeful; they suggest that our microbiome could be a powerful means for improving our health.”
~ Prof. Eran Segal of the Computer Science and Applied Mathematics Department
The field of microbiome research is relatively young; the database of 1,000 individuals collected at the Weizmann institute is one of the most extensive in the world. Segal and Elinav believe that over time, with the further addition of data to their study and those of others, these recent findings may be further validated, and the connection between our microbiome, our genetics and our health will become clearer.
Source: Rothschild D, Segal E et al. Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature. 2018 Mar 8;555(7695):210-215. doi: 10.1038/nature25973.