While it is understood that obesity is a risk factor for COVID-19 severity, there is new evidence that adipose tissue plays a key role in the aggravation of the virus and the development of a cytokine storm.
One of the theories under investigation is that fat cells (adipocytes) act as a reservoir for SARS-CoV-2 and increase viral load in obese or overweight individuals. Scientists also suspect that during infection fat cells release into the bloodstream substances that boost the inflammatory reaction triggered by the virus in the organism.

These hypotheses are being investigated by researchers at the University of São Paulo’s Medical School (FM-USP) in Brazil under the coordination of Marilia Cerqueira Leite Seelaender, a professor in the Department of Clinical Surgery. Peter Ratcliffe, a professor at the University of Oxford in the UK and one of the winners of the 2019 Nobel Prize for Medicine, is collaborating.
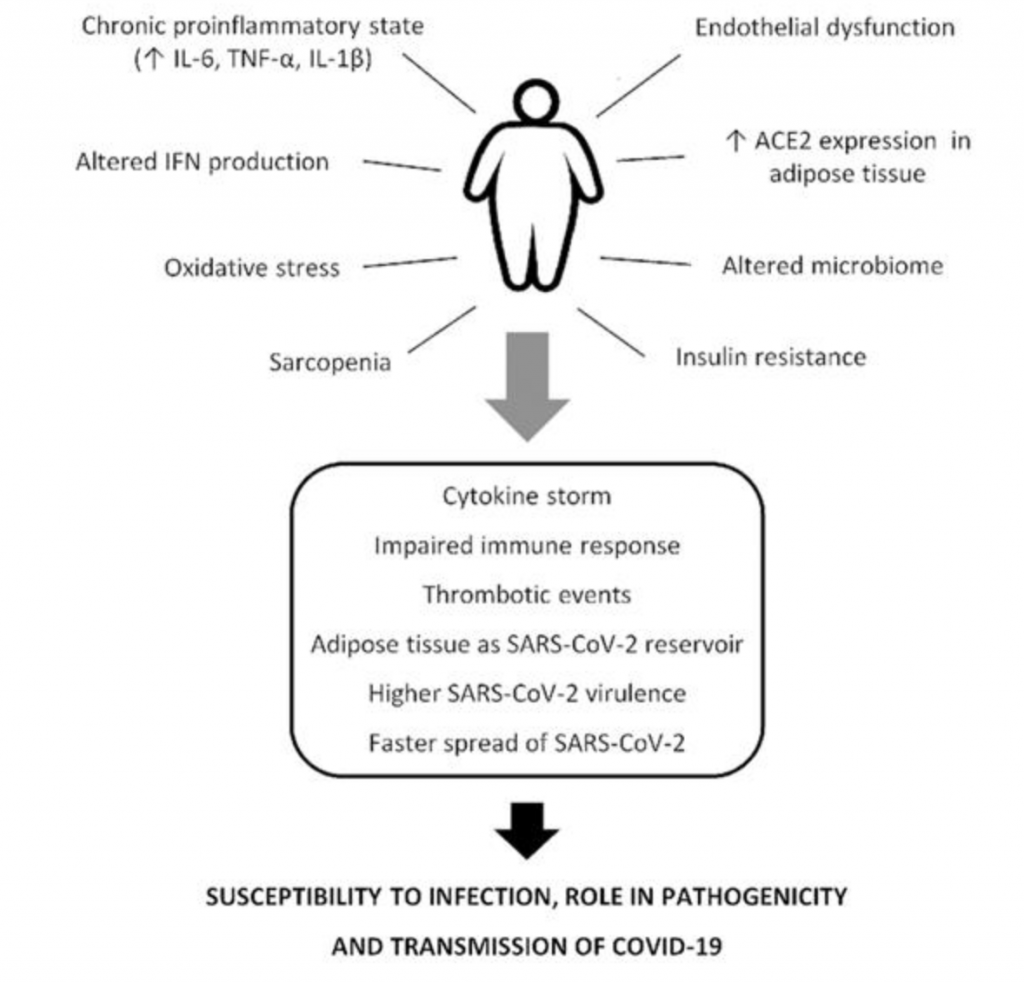
“A cytokine storm resulting in systemic inflammation similar to sepsis occurs in some severe COVID-19 patients. We believe these inflammatory factors come from adipose tissue. It’s been shown that when adipocytes expand too much, they can cause inflammation throughout the body, even in the brain,” Seelaender told Agência FAPESP.
- The FM-USP group analyzed samples of adipose tissue obtained from autopsies of people who died from COVID-19, and also from patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 who had to be submitted to emergency surgery at the university’s hospital for appendicitis or other reasons not related to the viral infection.
- Preliminary results confirmed that the virus can be found in fat cells, whose membranes are rich in ACE-2, the main receptor used by the virus to invade human cells.
- The researchers have yet to confirm that once it has invaded adipocytes, it can remain there long enough to replicate inside them.
FIGURE 1, Adipose Tissue and Inflammation
“It’s worth noting that visceral adipocytes have much more ACE2 than subcutaneous adipose tissue,” Seelaender said. “In addition, they’re much more inflammatory. As a result, visceral obesity tends to be even more harmful as far as COVID-19 is concerned.”
The preliminary findings also brought to light a change in the pattern of exosome secretion in the adipose tissue of infected people. Exosomes are extracellular vesicles, comparable to tiny bubbles, released by cells into the bloodstream with proteins and other types of signaling molecules. This is one of the mechanisms whereby information is exchanged between different tissues as the body adapts to changes in its environment.
Adipose Tissue Study Methods
The aims of the research conducted by the FM-USP group include investigating whether infection by SARS-CoV-2 makes adipocytes release more exosomes containing inflammatory factors. So far it has shown that the number of vesicles released into the bloodstream does indeed increase. The researchers will now analyze the contents of these circulating vesicles, as well as those remaining inside cells. They also plan to investigate the inflammatory pathways presumably activated by these molecules.
“We first assumed that as a person gets fat, their adipose tissue becomes hypoxic, meaning the person has less oxygen available. Hypoxia is itself a cause of inflammation, so one of the things we want to investigate is whether COVID-19 causes hypoxia in adipocytes,” Seelaender said.
Research on how human cells adapt to hypoxia won Ratcliffe the Nobel with William G. Kaelin (Harvard University) and Gregg Semenza (Johns Hopkins School of Medicine). Sir Radcliffe’s group is now interested in exploring the possibility that the SARS-CoV-2 virus interacts with hypoxia signalling pathways, and the Brazilian and British groups are collaborating as to address this hypothesis.

The FM-USP group, meanwhile, is concentrating on an effort to understand the effect of infection on adipose tissue. “We’re analyzing everything secreted by fat cells: proteins, saturated fatty acids, prostaglandins, microRNAs and exosomes,” Seelaender said.
Inflammatory factors released by adipose tissue in COVID-19 patients may be the cause of damage to the heart, lungs, and nervous system described in such patients, she added. “Our hypothesis is that obese COVID-19 patients undergo a similar process to that observed in the adipose tissue of patients with cachexia [significant rapid weight loss and muscle wasting associated with AIDS, heart failure and cancer, among other diseases],” she said.
“Adipocytes in cachexic individuals release more exosomes, and their contents are altered so that they have a pro-inflammatory profile. We know there’s inflammation in both cachexia and obesity. The difference lies in the type of inflammatory mediator released and the signaling pathways activated.”
Conclusion/ Healthy habits are important not only to ensure optimal immune response but also to prevent and/or treat undernutrition, obesity, and obesity-related comorbidities in COVID-19 patients. Therefore, clear advice on the impact of the nutritional status in COVID-19 outcomes should be provided to alert the population. Finally, it should be emphasized that nutritional status must be considered also in health policies designed to diminish the impact of COVID-19.