A nutraceutical study shows that chemical compounds in foods or beverages like green tea, muscadine grapes and dark chocolate can bind to and block protease function in SARS-CoV-2 virus, according to plant biologists at North Carolina State University.
“One of our lab’s focuses is to find nutraceuticals in food or medicinal plants that inhibit either how a virus attaches to human cells or the propagation of a virus in human cells,” said De-Yu Xie, professor of plant and microbial biology at NC State and the corresponding author of the study.
In the study, the NC State researchers performed both computer simulations and lab studies showing how the so-called “main protease” (Mpro) in the SARS-CoV-2 virus reacted when confronted with a number of different plant chemical compounds already known for their potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
“Mpro in SARS-CoV-2 is required for the virus to replicate and assemble itself,” Xie said. “If we can inhibit or deactivate this protease, the virus will die.”

Computer simulations showed that the studied chemical compounds from green tea, two varieties of muscadine grapes, cacao powder and dark chocolate were able to bind to different portions of Mpro.
“Mpro has a portion that is like a ‘pocket’ that was ‘filled’ by the chemical compounds,” Xie said. “When this pocket was filled, the protease lost its important function.”
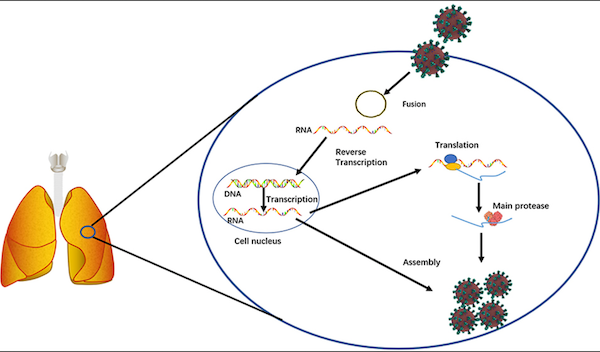
In vitro lab experiments completed by Yue Zhu, an NC State Ph.D. student in Xie’s lab, showed similar results. The chemical compounds in green tea and muscadine grapes were very successful at inhibiting Mpro’s function; chemical compounds in cacao powder and dark chocolate reduced Mpro activity by about half.
- Both docking simulation and in vitro assay showed that (–)-catechin-3-O-gallate (7), (–)-epicatechin-3-O-gallate (8), (–)-gallocatechin-3-O-gallate (9), and (–)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (10), procyanidin B1 (11) and B2 (12) inhibited the Mpro activity of SARS-Cov-2.
- Moreover, these compound-rich extracts of green tea, muscadine grape, cacao, and dark chocolate also inhibited the Mpro activity.

“Green tea has five tested chemical compounds that bind to different sites in the pocket on Mpro, essentially overwhelming it to inhibit its function,” Xie said. “Muscadine grapes contain these inhibitory chemicals in their skins and seeds. Plants use these compounds to protect themselves, so it is not surprising that plant leaves and skins contain these beneficial compounds.”
In summary, although these natural extracts have not been tested for the inhibitory efficacy in animals and humans, based on their inhibitory activity in vitro, we propose that an increased consumption of these common products might enhance reducing risk of SARS-Cov-2 and COVID-19.
Click Here for Full Text Study