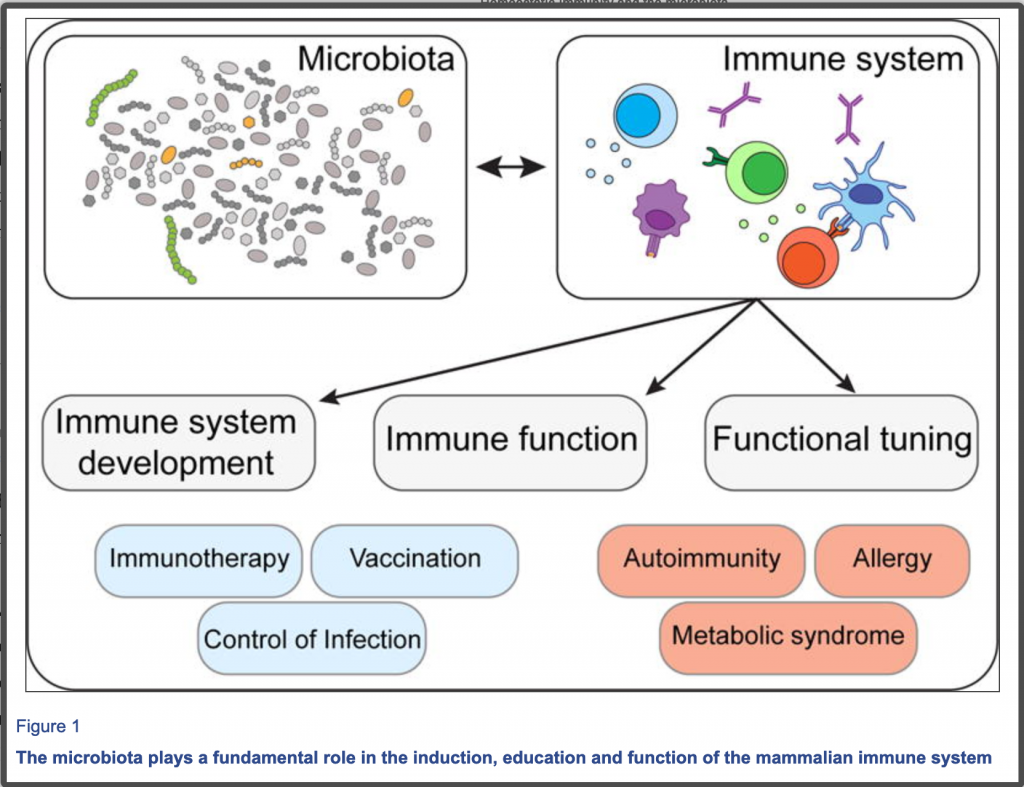
Can Selected Probiotic Strains Reduce Risk of Eczema in High-Risk Children?
Skin and allergic diseases are on the rise in children. One hypothesis is that there is reduced exposure to microbial components early in life. There are five clinical studies currently available regarding the primary prevention of atopic eczema using probiotic bacteria for allergic diseases. And none have shown promising results,Read