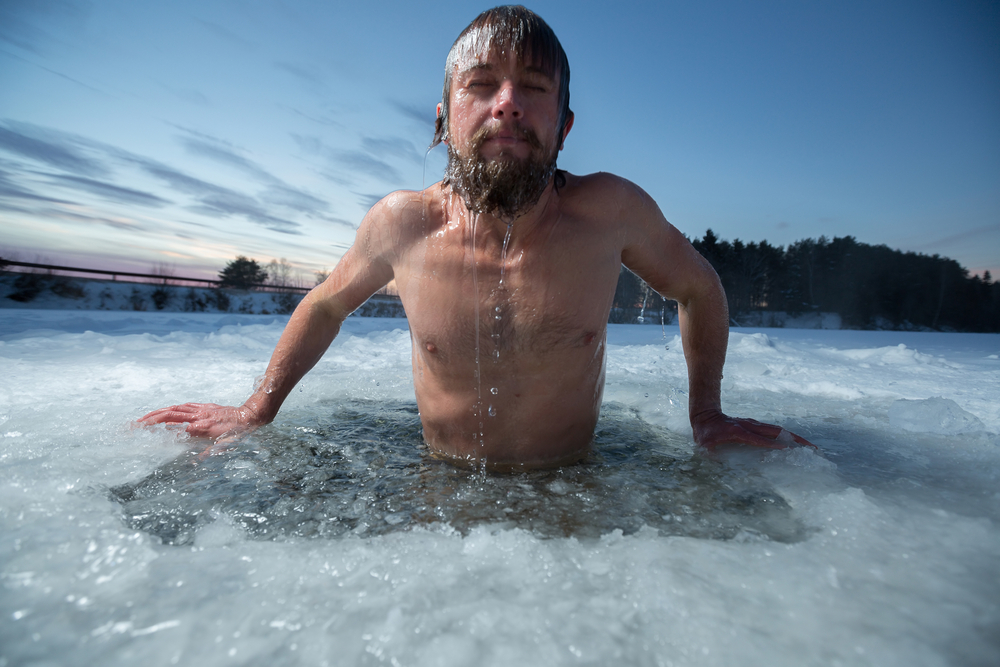
Icy Swims Reduce Body Fat, Diabetes Risk
Taking a cold-water swim may reduce “bad” body fat in men and lower the odds developing diabetes, according to a major scientific review published in the peer-reviewed International Journal of Circumpolar Health. The analysis included 104 studies and was conducted at the UiT The Arctic University of Norway and theRead